Nexus
🧭 Overview
This Nexus HAL (Hardware Abstraction Layer) provides an abstraction over a hardware component of a payment terminal (e.g., NFC, SmartCard, MSR, EMV, System etc.) >and exposes its operations via an AIDL interface. This allows other Android libraries or apps (especially system apps) to communicate with the hardware in a >consistent and secure manner, without needing to know the low-level implementation details.
The HAL handles all low-level communication with the hardware and provides a high-level, AIDL-based API to other components.
🔌 Purpose
Act as a service layer between Android applications and the underlying hardware.
Encapsulate hardware-specific logic.
Provide a stable AIDL interface for use by libraries.
Handle initialization, I/O, and error recovery.
🧩 Architecture
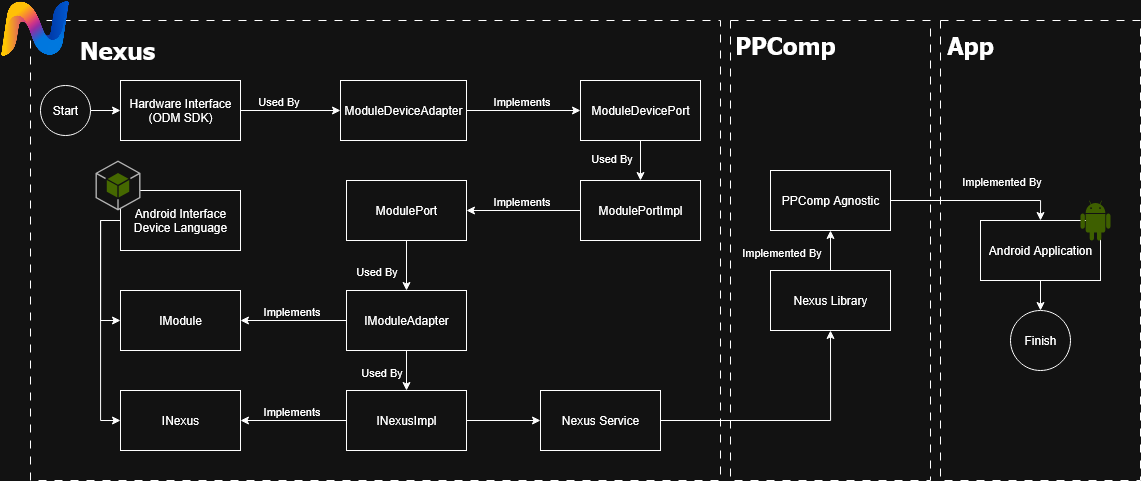
Each module is organized using the principles of hexagonal architecture, where communication between components is done through well-defined interfaces (ports) and their respective implementations (adapters).
The word "Module" will be used to substitute the respective module which can be EMV, CT, CL, MSR, System, Crypto, Tables.
The ModuleDeviceAdapter class implements the ModuleDevicePort interface. This class is responsible for interacting with the ODM SDK APIs to execute low-level operations.
The ModulePortImpl class implements the ModulePort interface. This is the input port of the module — the interface exposed to the outside world. It contains the business logic and orchestrates operations by calling the "ModuleDevicePort" to perform lower-level actions.
The IModuleAdapter class implements the IModule AIDL interface. It acts as an AIDL adapter, connecting the external Android AIDL layer to the internal use cases defined in ModulePort.
The INexusImpl class implements the INexus AIDL interface and serves as a central access point to all modules. It returns instances of each IModuleAdapter.
The NexusService class extends Android's Service and is responsible for binding the AIDL service. When a client binds to the service, it returns the binder for INexusImpl.
Nexus Core Service
NexusService – Main Android service responsible for hosting the Nexus AIDL interface and managing the lifecycle of all terminal operations. This service acts as the central entry point for client applications, exposing EMV, contact, contactless, MSR, system, cryptographic, and table operations through IPC, while coordinating access to hardware resources and underlying kernels.
Main Ports
In this service there is 7 main modules, each one responsible for a specific functionality. These modules are exposed through a ModulePort interface and implemented by a ModulePortImpl class.
The ports are:
EMVPort – Provides high-level EMV transaction operations for contact and contactless cards, including kernel initialization, tag management, application and CAPK loading, transaction parameter setup, callback handling, and execution of the EMV transaction flow (selection, record reading, 1st and 2nd Generate AC).
CTPort – Responsible for low-level operations with contact (chip) cards, such as powering the reader on or off, detecting card presence, and sending APDU commands.
CLPort – Responsible for low-level operations with contactless cards, including enabling or disabling the reader, detecting card presence, and exchanging APDU commands.
MsrPort – Handles magnetic stripe card operations, including reading tracks and reporting the last error for each track.
SystemPort – Provides access to terminal and system information, such as terminal identification, capabilities, EMV kernel versions (Mastercard, Visa, Amex, Discover, JCB, UnionPay), key presence and type (TDES or DUKPT), and KSN data for DUKPT keys.
CryptoPort – Handles cryptographic operations, including data encryption/decryption, key verification, secure PIN capture and PIN block generation, and DUKPT key management (KSN retrieval and increment), supporting both DUKPT and MK/SK TDES keys.
TablesPort – Manages transaction configuration tables, including supported EMV AIDs and parameters required for contact and contactless processing, with values mapped directly to their corresponding EMV tags.
Core Types and Error Handling
This section groups the core shared types used across the Nexus domain, including standardized return codes, callback contracts, and exception handling mechanisms.
NexusRet – Enumeration of return codes from Nexus methods, to map errors and behaviors.
INexusDspCallbacksPort – Interface for receiving text callbacks.
NexusException - Exception class for handling errors from Nexus methods.